Why should EMTs study pharmacology? The answer lies in the critical role they play in emergency medical services, where the safe and effective administration of medications can mean the difference between life and death. This guide delves into the importance of pharmacology for EMTs, exploring the types of medications they use, administration techniques, medication safety, and the essential educational requirements.
From understanding the legal and ethical responsibilities of medication administration to navigating the complexities of drug interactions, EMTs must possess a comprehensive knowledge of pharmacology. This guide provides a roadmap for EMTs to enhance their pharmacological expertise, ensuring they are equipped to provide the best possible care in emergency situations.
Importance of Pharmacology for EMTs
Pharmacology plays a vital role in emergency medical services, as it provides EMTs with the knowledge and skills to administer medications safely and effectively. Understanding the principles of pharmacology is essential for EMTs to fulfill their responsibilities and provide optimal patient care.
Legal and Ethical Responsibilities
EMTs have legal and ethical responsibilities when administering medications. They must:
- Obtain valid orders from a licensed healthcare provider.
- Verify the patient’s identity, medication, and dosage.
- Administer medications according to the prescribed route and method.
- Monitor the patient for adverse reactions and provide appropriate interventions.
- Document all medication administrations accurately.
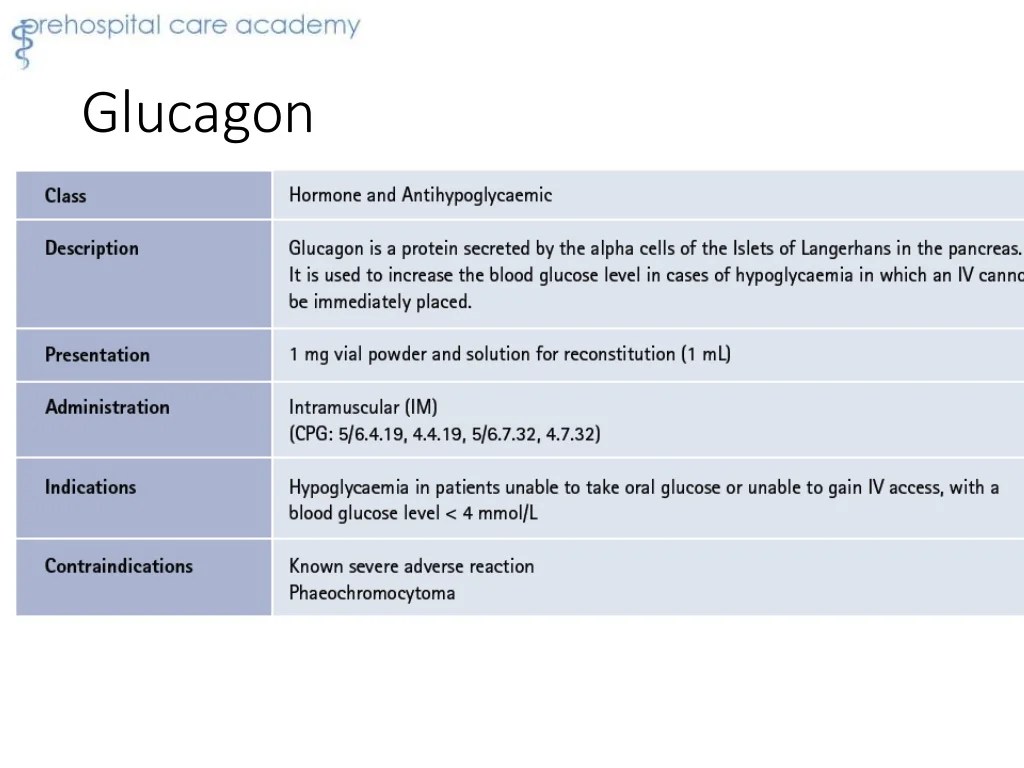
Types of Medications Used by EMTs
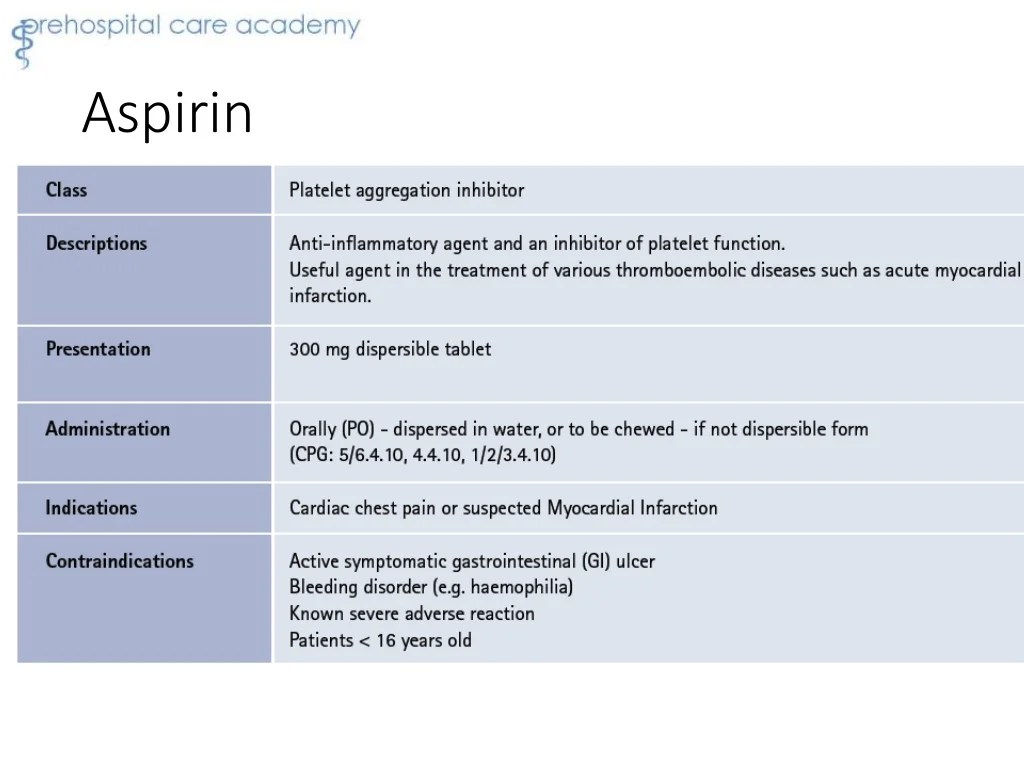
Emergency medical technicians (EMTs) administer a wide range of medications to treat various medical conditions. These medications fall into several categories, each with its own specific uses and indications.
Analgesics
- Acetaminophen: Pain reliever and fever reducer
- Ibuprofen: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) for pain and inflammation
- Morphine: Opioid pain reliever for severe pain
Antihistamines
- Diphenhydramine: Allergy and motion sickness relief
- Loratadine: Long-acting antihistamine for seasonal allergies
Bronchodilators
- Albuterol: Inhaler for asthma and COPD
- Salmeterol: Long-acting bronchodilator for asthma
Cardiovascular Medications
- Aspirin: Antiplatelet medication to prevent blood clots
- Nitroglycerin: Vasodilator for chest pain
- Amiodarone: Antiarrhythmic medication to control irregular heartbeats
Electrolytes
- Sodium chloride: Intravenous fluid to restore fluid and electrolyte balance
- Potassium chloride: Intravenous medication to treat hypokalemia
Gastrointestinal Medications
- Ondansetron: Antiemetic for nausea and vomiting
- Metoclopramide: Prokinetic medication to improve stomach emptying
Glucocorticoids
- Hydrocortisone: Anti-inflammatory medication for allergic reactions and asthma
- Dexamethasone: Steroid medication for severe inflammation
Medication Administration Techniques
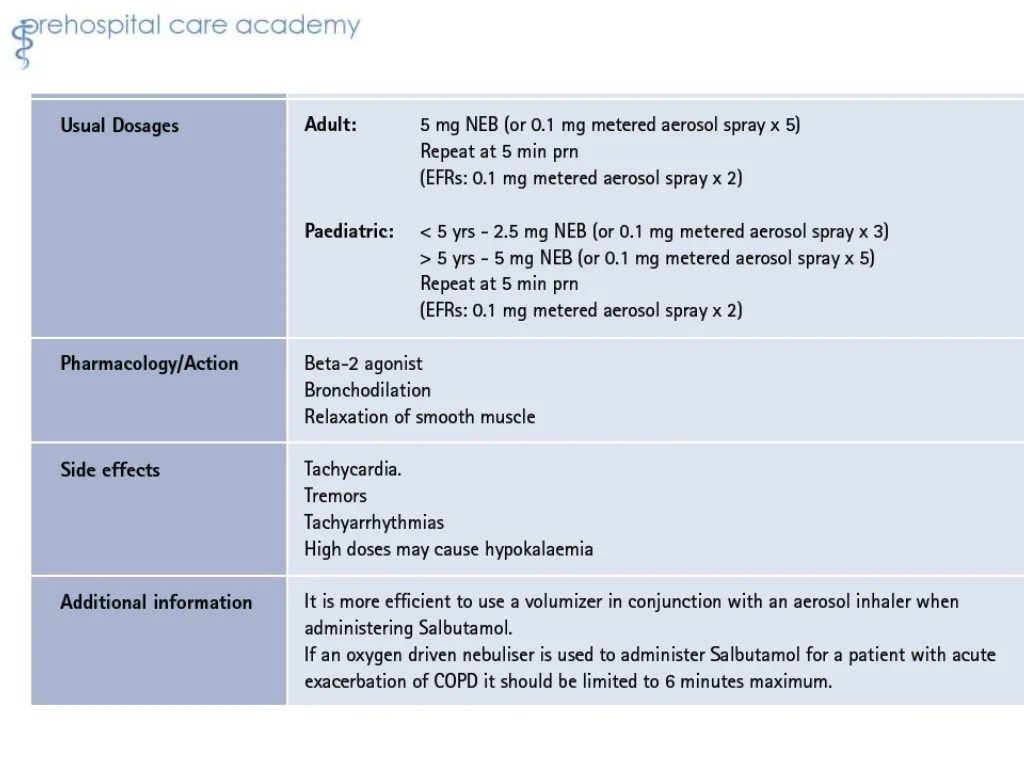
EMTs administer medications to patients using various techniques, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of administration method depends on several factors, including the type of medication, the patient’s condition, and the availability of equipment.
The most common methods of medication administration used by EMTs include:
Oral Administration
Oral administration involves giving the medication by mouth. This is the most common method and is used for medications that can be absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract. Oral administration is convenient and non-invasive, but it can be difficult for patients who are unable to swallow or who are vomiting.
Sublingual Administration
Sublingual administration involves placing the medication under the tongue. This allows the medication to be absorbed directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract. Sublingual administration is used for medications that need to be absorbed quickly, such as nitroglycerin for chest pain.
Buccal Administration
Buccal administration involves placing the medication between the cheek and gum. This allows the medication to be absorbed directly into the bloodstream, similar to sublingual administration. Buccal administration is used for medications that need to be absorbed slowly, such as fentanyl for pain relief.
Transdermal Administration
Transdermal administration involves applying the medication to the skin. This allows the medication to be absorbed directly into the bloodstream through the skin. Transdermal administration is used for medications that need to be delivered over a long period of time, such as nicotine patches for smoking cessation.
Intramuscular Administration
Intramuscular administration involves injecting the medication into a muscle. This allows the medication to be absorbed directly into the bloodstream. Intramuscular administration is used for medications that need to be delivered quickly, such as epinephrine for anaphylaxis.
Intravenous Administration
Intravenous administration involves injecting the medication directly into a vein. This allows the medication to be delivered directly into the bloodstream. Intravenous administration is used for medications that need to be delivered very quickly, such as vasopressors for shock.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Administration Method, Why should emts study pharmacology
The choice of administration method depends on several factors, including:
- The type of medication
- The patient’s condition
- The availability of equipment
- The EMT’s training and experience
EMTs must be familiar with the different methods of medication administration and the factors that influence the choice of method. By using the appropriate administration method, EMTs can ensure that patients receive the medications they need in a safe and effective manner.
Medication Safety

Medication safety is paramount in emergency medical services (EMS) as medications can have significant effects on patients’ health. EMTs must adhere to strict protocols and guidelines to ensure the safe and effective administration of medications.
Potential Risks and Complications
Medication administration carries potential risks and complications, including:
-
-*Allergic reactions
Some patients may be allergic to certain medications, which can cause anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening reaction.
-*Overdose
Administering too much of a medication can lead to toxicity and adverse effects.
-*Underdose
Administering too little of a medication may not provide the desired therapeutic effect.
-*Drug interactions
Certain medications can interact with each other, leading to altered effects or side effects.
-*Improper administration
Incorrect administration techniques, such as giving a medication via the wrong route or at the wrong time, can compromise its effectiveness and safety.
EMTs must be aware of these risks and take appropriate precautions to mitigate them. This includes obtaining a thorough patient history, checking for allergies, calculating dosages accurately, and monitoring patients closely for adverse reactions.
Medication Interactions
Medication interactions occur when two or more drugs taken together produce an effect that is different from the intended effect of either drug alone. This can result in reduced effectiveness, increased side effects, or even toxicity.
In emergency medical services, medication interactions are a potential concern due to the variety of medications that may be administered in a short period of time. Some common drug interactions include:
Antiplatelet Medications and Anticoagulants
- Taking antiplatelet medications (such as aspirin or clopidogrel) with anticoagulants (such as warfarin or heparin) can increase the risk of bleeding.
- This is because both types of medications interfere with the blood’s ability to clot.
Opioid Pain Relievers and Benzodiazepines
- Taking opioid pain relievers (such as morphine or oxycodone) with benzodiazepines (such as lorazepam or diazepam) can increase the risk of respiratory depression.
- This is because both types of medications slow down the respiratory rate.
Antihypertensive Medications and Diuretics
- Taking antihypertensive medications (such as ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers) with diuretics (such as furosemide or hydrochlorothiazide) can increase the risk of hypotension.
- This is because diuretics can cause dehydration, which can lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
It is important for EMTs to be aware of potential medication interactions and to take steps to avoid them. This includes checking for drug interactions before administering any medications and monitoring patients for signs of adverse reactions.
Pharmacology Education for EMTs: Why Should Emts Study Pharmacology

To ensure safe and effective medication administration, EMTs must possess a thorough understanding of pharmacology. This includes knowledge of drug actions, interactions, and potential side effects.
EMT training programs typically include a comprehensive pharmacology component, covering essential topics such as drug classifications, dosage calculations, and administration techniques. Additionally, EMTs are required to complete continuing education courses in pharmacology to maintain their certification.
Educational Requirements
- EMTs must complete an accredited EMT training program that includes a pharmacology component.
- EMTs must pass a national certification exam that includes pharmacology content.
- EMTs must complete continuing education courses in pharmacology to maintain their certification.
Importance of Continuing Education
Continuing education in pharmacology is essential for EMTs to stay up-to-date on the latest medications and their uses. It also provides an opportunity to review and reinforce previously learned material.
- New medications are constantly being developed, and EMTs need to be aware of their properties and potential side effects.
- Continuing education courses can help EMTs improve their medication administration skills.
- Continuing education can help EMTs stay up-to-date on the latest guidelines and best practices for medication administration.
Question & Answer Hub
Why is pharmacology important for EMTs?
Pharmacology provides EMTs with the knowledge and skills to safely and effectively administer medications in emergency situations, potentially saving lives and improving patient outcomes.
What are the different types of medications used by EMTs?
EMTs use a wide range of medications, including pain relievers, anti-nausea medications, anti-anxiety medications, and medications for cardiac and respiratory emergencies.
How do EMTs administer medications?
EMTs can administer medications through various routes, including oral, intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous injections.
What are the potential risks and complications of medication administration?
Medication administration can pose risks such as allergic reactions, drug interactions, and adverse side effects. EMTs must be aware of these risks and take appropriate precautions to ensure patient safety.
What are the educational requirements for EMTs to administer medications?
EMTs must complete specific training programs and pass certification exams to be authorized to administer medications.