Europe before and after ww1 worksheet answers – Unveiling the transformative era of Europe before and after WWI, this comprehensive guide delves into the political, economic, and social landscapes that shaped the continent during this tumultuous period.
From the intricate alliances and rivalries that ignited the Great War to the profound impact of its aftermath, this narrative provides a captivating exploration of a pivotal chapter in European history.
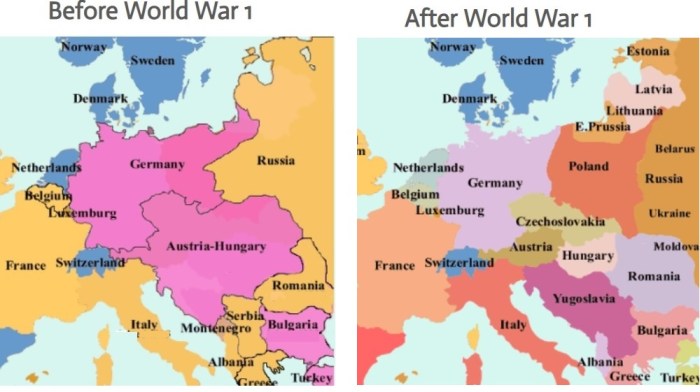
Pre-World War I Europe
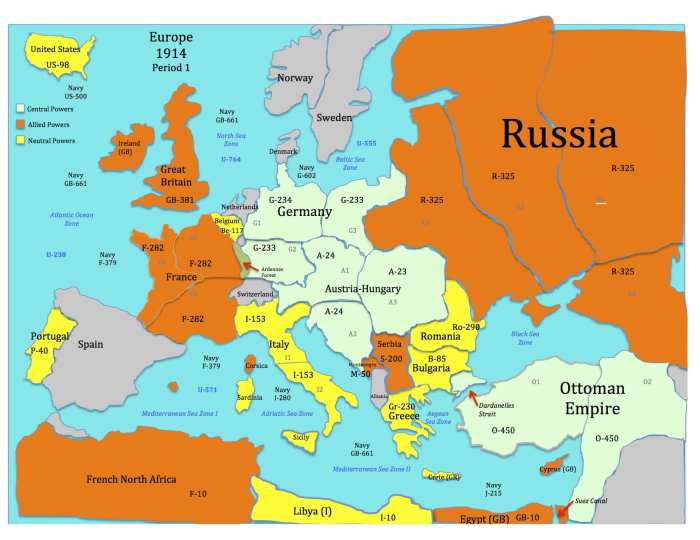
Before the outbreak of World War I in 1914, Europe was a continent of great powers, each with its own ambitions and rivalries. The major powers included Great Britain, France, Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Russia.
These powers were bound together by a complex web of political and economic alliances. The most important of these alliances was the Triple Alliance, which linked Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. The Triple Entente, on the other hand, was a loose alliance between Great Britain, France, and Russia.
Tensions and rivalries between the European powers were also on the rise. Germany, a rapidly industrializing nation, was challenging the dominance of Great Britain. France was seeking to regain Alsace-Lorraine, which had been lost to Germany in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870-1871.
Austria-Hungary was facing growing nationalist movements within its multi-ethnic empire.
The Outbreak of World War I
The immediate cause of the outbreak of World War I was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, on June 28, 1914. The assassination was carried out by a Serbian nationalist, Gavrilo Princip. Austria-Hungary, with the backing of Germany, responded by declaring war on Serbia.
Nationalism and imperialism played a major role in the outbreak of the war. Nationalism led to a sense of national pride and rivalry among the European powers. Imperialism, the desire to acquire and control overseas colonies, also contributed to tensions between the powers.
The Course of World War I
World War I was one of the most destructive conflicts in history. The war was fought on two main fronts: the Western Front, in France and Belgium, and the Eastern Front, in Russia. The war also spread to other parts of the world, including the Middle East and Africa.
New technologies, such as machine guns, poison gas, and airplanes, were used in the war. These technologies made the war more deadly and destructive.
The war had a devastating impact on the civilian population. Millions of people were killed, wounded, or displaced from their homes. The war also caused widespread economic disruption.
The End of World War I
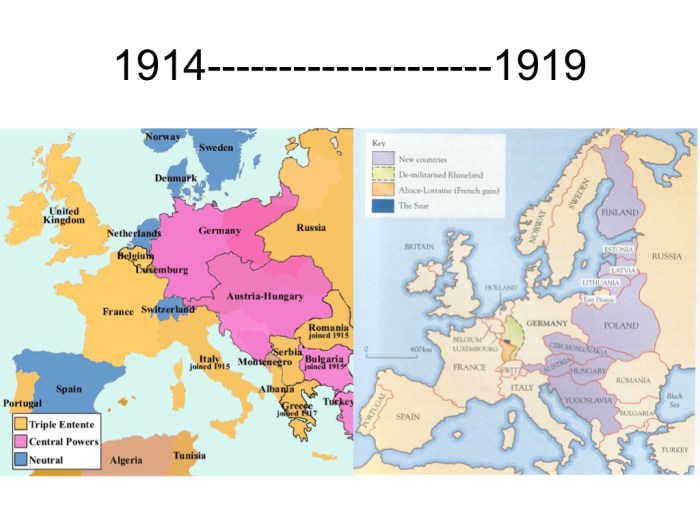
World War I ended on November 11, 1918, with the signing of an armistice between the Allies and Germany. The armistice was followed by the Treaty of Versailles, which was signed in 1919. The treaty imposed harsh penalties on Germany, including the loss of territory and the payment of reparations.
The war had a profound impact on Europe and the world. The war led to the collapse of the Russian, German, and Austro-Hungarian empires. It also led to the rise of new ideologies, such as communism and fascism.
Post-World War I Europe: Europe Before And After Ww1 Worksheet Answers
After World War I, Europe was a continent in turmoil. The war had left behind a legacy of political and economic instability. The war also led to the rise of new ideologies, such as communism and fascism.
Europe faced a number of challenges in the aftermath of the war. These challenges included the need to rebuild the war-torn economies, the need to address the social and political unrest that had been caused by the war, and the need to prevent the outbreak of another war.
Helpful Answers
What were the major causes of World War I?
Nationalism, imperialism, militarism, and the intricate web of alliances between European powers.
How did the Treaty of Versailles impact Europe?
It imposed harsh reparations on Germany, redrew national boundaries, and sowed the seeds of future conflict.
What were the key challenges faced by Europe after WWI?
Economic instability, political upheaval, the rise of extremist ideologies, and the need to rebuild war-torn societies.