Unit 1 geometry basics homework 2 segment addition postulate answers – Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2: Segment Addition Postulate Answers delves into the fundamental principles of geometry, providing a comprehensive understanding of the segment addition postulate and its applications. This guide offers clear explanations, detailed examples, and insightful discussions to empower students in mastering this essential concept.
Through a systematic approach, this guide explores the segment addition postulate, its significance in geometry, and its limitations. It also provides step-by-step solutions to the problems in Homework 2, addressing common mistakes and fostering a deeper comprehension of the subject matter.
Segment Addition Postulate
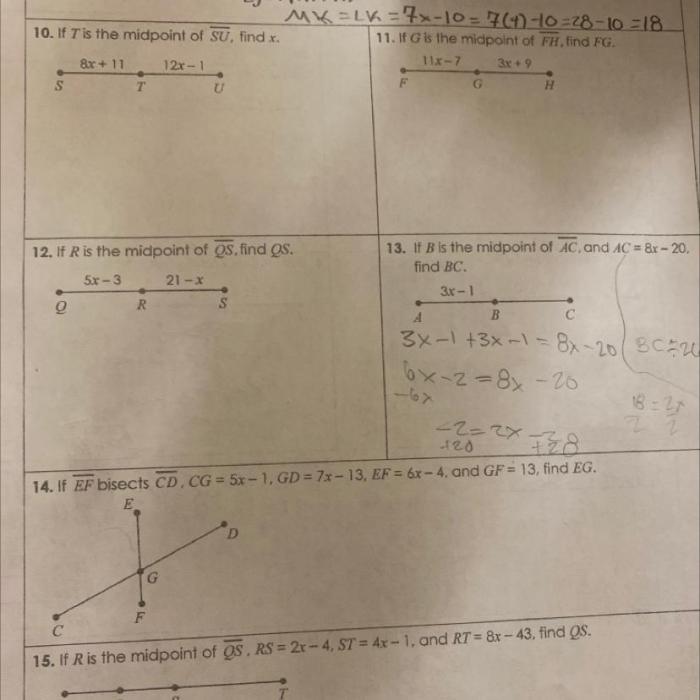
The segment addition postulate states that if a point C is between points A and B on a line, then the distance from A to C plus the distance from C to B is equal to the distance from A to B.
In other words, if AC+ CB= AB, then point C is between points A and B on a line.
Examples
- If AC= 3 cm and CB= 4 cm, then AB= 7 cm.
- If AB= 10 cm and CB= 6 cm, then AC= 4 cm.
Limitations
The segment addition postulate does not apply to all points on a line. For example, if point C is not between points A and B, then the segment addition postulate does not apply.
Homework 2 Answers
Problem 1:Find the length of ABif AC= 3 cm and CB= 4 cm.
Answer: AB= 7 cm
Steps:
- Use the segment addition postulate: AC+ CB= AB.
- Substitute the given values: 3 cm + 4 cm = AB.
- Simplify: AB= 7 cm.
Problem 2:Find the length of ACif AB= 10 cm and CB= 6 cm.
Answer: AC= 4 cm
Steps:
- Use the segment addition postulate: AC+ CB= AB.
- Substitute the given values: AC+ 6 cm = 10 cm.
- Subtract 6 cm from both sides: AC= 4 cm.
Common Mistakes:
- Forgetting to use the segment addition postulate.
- Substituting the incorrect values into the segment addition postulate.
- Making errors in simplifying the equation.
Geometry Basics

Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and relationships of points, lines, planes, and solids.
Points, Lines, and Planes
A point is a location in space. A line is a straight path that extends infinitely in both directions. A plane is a flat surface that extends infinitely in all directions.
Angles and Triangles, Unit 1 geometry basics homework 2 segment addition postulate answers
An angle is formed by two rays that share a common endpoint. A triangle is a polygon with three sides.
Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
Unit 1 Review: Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2 Segment Addition Postulate Answers
Unit 1 covered the following key concepts:
- The segment addition postulate
- The basics of geometry
- Angles and triangles
- The Pythagorean theorem
Students who need additional support may want to review the following resources:
- The textbook
- The class notes
- Online tutorials
Q&A
What is the segment addition postulate?
The segment addition postulate states that if a point C lies between points A and B on a line, then the length of the line segment AB is equal to the sum of the lengths of the line segments AC and CB.
How is the segment addition postulate used in geometry?
The segment addition postulate is used to find the length of a line segment when the lengths of two shorter segments that make up the longer segment are known.
What are the limitations of the segment addition postulate?
The segment addition postulate only applies to line segments that lie on the same line.