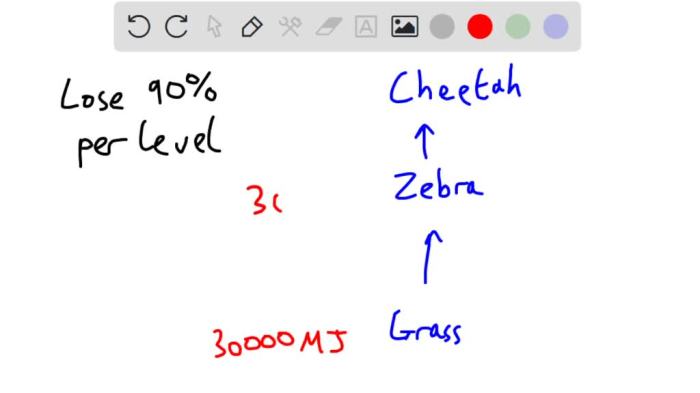
Grass starts with 30000 kcal of energy – Grass starts with 30,000 kcal of energy, a remarkable endowment that fuels ecosystems and sustains life on Earth. As the primary producer in grasslands, grass plays a pivotal role in the energy flow that supports a vast array of organisms.
This article delves into the energy content of grass, exploring its ecological significance and implications for biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Grasslands, vast expanses dominated by grasses, are among the most productive ecosystems on the planet. Grass, with its abundant energy reserves, forms the foundation of these ecosystems, providing sustenance for herbivores and shaping the intricate web of life that thrives within them.
1. Introduction
Energy is a fundamental aspect of all ecosystems, driving the biological processes that sustain life. Gross primary production (GPP) refers to the total amount of energy captured and stored by plants through photosynthesis. Grass, as a dominant vegetation type in many ecosystems, plays a significant role in GPP.
Grasslands, characterized by the prevalence of grasses, are important biomes that contribute substantially to global energy production. These ecosystems support a diverse range of herbivores, which utilize grass energy to sustain their populations.
2. Energy Flow in Grasslands

Energy flow in grasslands follows a unidirectional pattern, with energy transferred from producers (plants) to consumers (herbivores) and subsequently to higher trophic levels.
Grass, as a primary producer, captures solar energy through photosynthesis and converts it into chemical energy stored in its tissues. This energy is then transferred to herbivores, which consume grass and extract the stored energy through digestion.
3. Energy Content of Grass
The energy content of grass varies depending on factors such as species, maturity, and environmental conditions. On average, grass contains approximately 30,000 kcal of energy per kilogram of dry matter.
Grass stores energy primarily in the form of carbohydrates, including cellulose, hemicellulose, and starch. These carbohydrates provide a rich source of energy for herbivores.
4. Utilization of Grass Energy
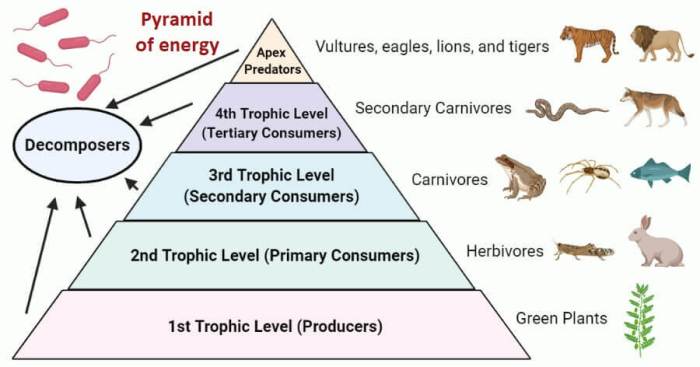
Herbivores utilize grass energy through the process of digestion. Their digestive systems have evolved to break down the tough plant fibers and extract the energy stored within.
The efficiency of energy transfer between grass and herbivores is typically low, with only a small percentage of the energy consumed actually being converted into biomass. However, this energy transfer is essential for supporting herbivore populations and maintaining ecosystem balance.
5. Ecological Implications
The high energy content of grass has significant ecological implications:
- Supports biodiversity:Grass provides a food source for a wide range of herbivores, which in turn support predators and other organisms.
- Ecosystem stability:Grasslands act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass. This helps regulate the global carbon cycle and mitigate climate change.
- Nutrient cycling:Grasslands facilitate nutrient cycling by capturing and releasing nutrients back into the soil, enhancing soil fertility.
Common Queries: Grass Starts With 30000 Kcal Of Energy
What is gross primary production (GPP)?
GPP is the total amount of energy fixed by plants through photosynthesis in a given area over a specific period.
How does grass store energy?
Grass stores energy in the form of carbohydrates, primarily cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
What factors affect the energy content of grass?
Factors such as species, maturity, growing conditions, and environmental factors influence the energy content of grass.