Biochemistry basics pogil answer key – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of biochemistry with our comprehensive Pogil answer key. Delving into the fundamental concepts and principles of this captivating field, we unravel the intricate workings of life’s molecular machinery, empowering you with a deeper understanding of the chemical processes that govern our existence.
Through a meticulous analysis of the Pogil answer key’s structure and pedagogical approach, we illuminate the key concepts of biochemistry, from the building blocks of biomolecules to the intricate dance of enzyme catalysis. Prepare to witness the elegance of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation as we explore their pivotal roles in energy metabolism.
Biochemistry Basics
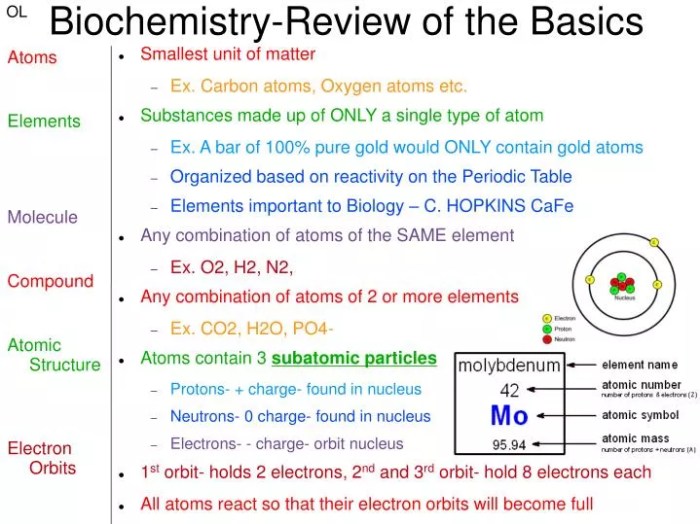
Biochemistry, the study of the chemical processes that occur within living organisms, provides a fundamental understanding of the molecular basis of life. It encompasses the structure, function, and interactions of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, which are essential for cellular function and metabolism.
Structure and Function of Biomolecules
Biomolecules are organic compounds that perform specific functions within cells. Carbohydrates, composed of sugars, provide energy and structural support. Lipids, including fats and oils, serve as energy reserves and form cell membranes. Proteins, made up of amino acids, are involved in a wide range of cellular processes, including catalysis, transport, and structural support.
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, store and transmit genetic information.
Enzyme Catalysis
Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts, facilitating biochemical reactions without being consumed. They increase the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur. Enzymes are highly specific, each catalyzing a particular reaction or group of related reactions.
Their importance lies in enabling essential biochemical reactions to proceed efficiently within cells.
Pogil Answer Key
The Pogil answer key for biochemistry basics is a comprehensive resource that provides detailed solutions to the activities and exercises in the Pogil biochemistry basics module. It is designed to help students understand the key concepts and principles of biochemistry and to assess their progress.
The answer key is organized into sections that correspond to the chapters in the Pogil biochemistry basics module. Each section includes a brief overview of the chapter’s key concepts and a detailed answer key for the activities and exercises in that chapter.
Pedagogical Approach
The Pogil activities and exercises are designed to be student-centered and inquiry-based. They encourage students to actively engage with the material and to develop their critical thinking skills. The answer key provides detailed solutions to the activities and exercises, but it also includes explanations and discussions that help students to understand the concepts behind the answers.
Key Concepts in Biochemistry
Biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes that occur within living organisms. It is a vast and complex field that encompasses a wide range of topics, from the structure and function of proteins to the regulation of metabolism. In this section, we will provide a brief overview of some of the key concepts in biochemistry.
pH and Biological Systems, Biochemistry basics pogil answer key
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration ([H+]). The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most alkaline (also known as basic).
The pH of pure water is 7, which is considered neutral.
pH is a critical factor in many biological systems. For example, the pH of the blood is tightly regulated between 7.35 and 7.45. Small changes in blood pH can have a significant impact on the function of enzymes and other proteins.
Glycolysis, the Citric Acid Cycle, and Oxidative Phosphorylation
Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation are three key metabolic pathways that generate energy for cells. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose, a sugar molecule, into two molecules of pyruvate. The citric acid cycle is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of cells and result in the production of carbon dioxide and ATP.
Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that occurs in the mitochondria and uses the energy from the citric acid cycle to generate ATP.
These three pathways are essential for the survival of cells. They provide the energy that cells need to carry out their functions, such as muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and cell division.
ATP as an Energy Currency
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a molecule that serves as the energy currency of cells. ATP is a high-energy molecule that can be broken down to release energy when needed. Cells use ATP to power a wide range of cellular processes, such as muscle contraction, protein synthesis, and cell division.
The ATP cycle is a continuous process that involves the breakdown and synthesis of ATP. Cells use ATP to store and release energy as needed.
Applications of Biochemistry
Biochemistry finds widespread applications in various fields, including medicine, biotechnology, and agriculture. Understanding biochemical principles allows scientists and researchers to develop new drugs, therapies, and diagnostic tools to address health challenges and improve human well-being.
Biotechnology utilizes biochemical principles to manipulate and modify living organisms or their components to create products or processes that benefit society. This field has led to advancements in genetic engineering, protein production, and the development of biofuels.
Medicine
- Drug Development:Biochemistry plays a crucial role in drug discovery and development. By understanding the biochemical pathways involved in diseases, scientists can design drugs that target specific molecules or processes to treat or prevent illnesses.
- Diagnostics:Biochemical tests are used to diagnose various diseases by analyzing blood, urine, or tissue samples. These tests detect specific biochemical markers or changes in biochemical processes associated with particular health conditions.
- Gene Therapy:Advances in biochemistry have enabled the development of gene therapy, which involves modifying or replacing faulty genes to treat genetic disorders.
Biotechnology
- Genetic Engineering:Biochemistry provides the foundation for genetic engineering techniques, such as recombinant DNA technology and gene editing, which allow scientists to modify the genetic makeup of organisms for research or industrial applications.
- Protein Production:Biochemical principles are used to optimize protein production in microorganisms or cell cultures for various purposes, including pharmaceuticals, industrial enzymes, and food additives.
- Biofuels:Biochemistry contributes to the development of biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, by understanding the biochemical processes involved in plant growth and fermentation.
Agriculture
- Crop Improvement:Biochemistry helps improve crop yield and quality by understanding the biochemical processes involved in plant growth, photosynthesis, and nutrient uptake.
- Pest Control:Biochemical principles are applied in developing environmentally friendly pest control methods by targeting specific biochemical pathways in pests.
- Soil Management:Biochemistry aids in understanding soil chemistry and nutrient cycling, enabling farmers to optimize soil fertility and crop production.
Ethical Implications
Advancements in biochemistry and biotechnology raise ethical considerations, including:
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs):The use of GMOs in agriculture and food production has sparked debates about their potential environmental and health impacts.
- Gene Editing:Ethical concerns surround the use of gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, for human applications and the potential for unintended consequences.
- Access to Healthcare:Ensuring equitable access to the benefits of biochemical advancements, such as new drugs and therapies, is a significant ethical challenge.
FAQ Corner: Biochemistry Basics Pogil Answer Key
What is the significance of pH in biochemistry?
pH plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and functionality of biomolecules. It affects enzyme activity, protein structure, and the ionization states of molecules, influencing various biological processes.
How does the citric acid cycle contribute to energy production?
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a key metabolic pathway that generates energy in the form of ATP. It involves a series of enzymatic reactions that oxidize acetyl-CoA, releasing carbon dioxide and generating high-energy electron carriers.